Answer these simple questions and we will find you the BEST prices
Which type of solar quotes do you need?
It only takes 30 seconds
100% free with no obligation

Tell us what you need to find a matching specialist

Get free quotes from professionals near you

Compare offers and choose the one that best matches your need
- whatcost.co.uk
- Home Insulation
- Insulation Building Regulations
Insulation Building Regulations: A Complete Guide 2026


- Part L of the UK Building Regulations outlines requirements for optimal home insulation, including u-value thresholds, insulation thickness, and safety measures.
- Effective wall, floor and roof insulation can save the detached UK home up to £900 in energy bill savings, and 2.4 tonnes in carbon cuts.
- Failure to comply with building regulations for insulation can result in penalties, expensive replacements, or even pose a risk to your home's structural integrity.
Home insulation has become a frontline to combat rising energy insecurity and soaring bills in the UK. In line with the ambitious Net Zero by 2050 goal, the UK housing stock is dramatically transitioning towards energy efficiency and sustainability.
But what rules and regulations govern home insulation? How can you ensure you’re current on what is expected? This complete guide by WhatCost will provide you with the most up-to-date building regulations and insulation demands.
Ready to insulate your home? WhatCost is here to help. Save yourself endless hours of research and vetting by spending just 30 seconds to fill out our online intake form. In return, we’ll send you up to 3 free home-tailored quotes from our nationwide network of trusted professionals. No costs or obligations apply. Simply click below to begin!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



Building regulations for insulation in the UK
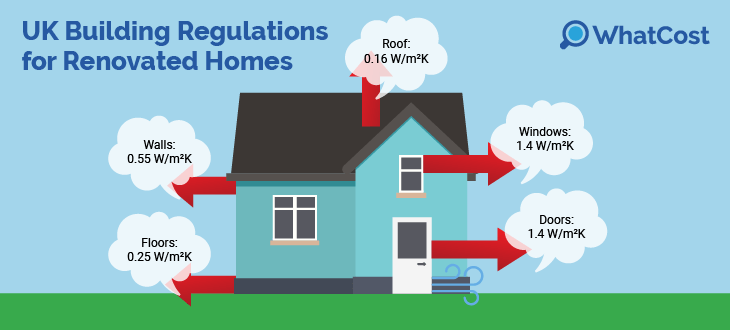
The UK Building Regulations outline a range of requirements for construction safety in both the commercial and residential spheres, with Part L of the documents focusing specifically on insulation measures.
These measures may differ depending on your home type (e.g. newly built or refurbished), chosen insulation, and the type of job carried out. The best way to ensure you meet requirements is to work with a professional installer who can tailor an approach suited to your budget and needs.
To get things started, here’s a breakdown of the expected u-values that building regs insulation expects, depending on whether the house is a new build or a renovation of an older property:
| Home area | New builds | Refurbishments |
|---|---|---|
| Solid walls | 0.26 W/m²K | 0.30 W/m²K |
| Cavity walls | 0.26 W/m²K | 0.55 W/m²K |
| Roof | 0.11 W/m²K | 0.16 W/m²K |
| Floors | 0.11 W/m²K | 0.25 W/m²K |
| Windows | 0.16 W/m²K | 1.4 W/m²K |
| Doors | 0.16 W/m²K | 1.4 W/m²K |
The u-value is the rate by which a material can prevent heat transfer. A lower value indicates a better insulation capacity.
Regulations for insulation thickness
The thickness of insulation that is installed is directly proportional to the u-value to be achieved. This means that insulation thickness can vary greatly depending on the material you use.
For example, 270mm of mineral wool and 120mm of PIR board can achieve the same u-value in many cases, except that you require much less thickness of the latter material. Here’s a summary of the average building regulations insulation thickness you can expect per job.
Wall insulation
Wall insulation is most often carried out by the use of mineral wool or other similar blanket-style insulation material. This is because it's easy to install, relatively inexpensive, and sustainable. Here’s a breakdown of what you could expect from internal, external, and cavity wall insulation regulations:
| Area of home | Recommended blanket insulation thickness |
|---|---|
| Internal solid wall insulation | 100mm |
| External solid wall insulation | 100mm |
| Cavity wall insulation | 150mm |
Roof insulation
Roof insulation measures are popularly carried out by using mineral wool or similar blanket-style insulation, however, rigid boards such as PIR and EPS polystyrene have become more popular in recent years. Loft insulation regulations tend to follow the same outlines as roof insulation regulations. Here’s a breakdown of the thicknesses you can expect to need as per roof insulation building regs:
| Material | New builds (0.11 W/m²K) | Retrofitting (0.15 W/m²K) | Renovations (0.16 W/m²K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPS polystyrene | 220-250mm | 250-280mm | 100-120mm |
| PIR board | 130-150mm | 150-170mm | 80-100mm |
| Mineral wool | 230-270mm | 270-290mm | 120-130mm |
Floor insulation
Floor insulation helps to cut a further 8-10% of home heat loss. To achieve this, various insulation materials can be used at varying thicknesses depending on the heat retention capacity of the material. Here’s a breakdown of expectations set out by building regs for floor insulation:
| Insulation material | Recommended thickness |
|---|---|
| Mineral wool | 150mm + |
| PIR board | 90mm + |
| Spray foam | 70mm + |
Steps to ensure compliance with insulation building regulations

Adhering to insulation building regs is crucial for maximising energy efficiency, enhancing home comfort, and ensuring long-term value. Here are key steps to achieve compliance and a successful installation:
- Seek multiple quotes: Carefully research and compare multiple insulation installers. Obtain detailed quotes from each installer, comparing costs, materials, and methods. Too expensive? Grants for insulation like the GBIS or ECO4 exist to help low-income and fuel-poor houses with financial assistance.
- Verify credentials: Ensure all potential installers are properly accredited and certified, demonstrating their expertise and adherence to industry standards. Investigate their past work through online reviews and previous jobs to assess their professionalism.
- Prioritise professional expertise: While DIY options may seem tempting, professional installation often ensures optimal results, minimises risks, and guarantees compliance with building regulations. It’s best to hire a reputable and experienced insulation contractor.
- Conduct a home inspection: Insist on a thorough assessment of your home's needs by the chosen installer. This assessment will help identify any existing problems, such as air leaks or structural deficiencies, that may impact insulation performance.
Unfortunately, not many prospective customers have endless hours to give to research and vetting, ultimately settling for high prices and low-quality jobs. That’s why WhatCost can be your one-stop solution for all your needs!
All you need is 30 seconds to fill out our online intake form, and we’ll send you up to 3 free home-tailored quotes directly from our network of trusted installers. No costs or obligations apply. Simply click below to begin!
- Describe your needs
- Get free quotes
- Choose the best offer
It only takes 30 seconds



FAQ
Building regulations for insulation enforce requirements that make sure your insulation is safe, effective and durable. Part L of the UK Building Regulations document outlines u-value requirements, insulation thicknesses, ventilation, and fire safety guidelines for insulation.
A key change in insulation regulations is that the minimum thickness of cavity wall insulation was raised to 150mm, from the previous 100mm. This is in line with more stringent requirements on u-value that need to be achieved.
The minimum thickness of home insulation depends on several factors, such as the area of the home being insulated, the chosen insulation material, and the u-value that must be achieved. For example, most roof and loft jobs will require around 270mm of blanket insulation to achieve the recommended u-value.
The minimum wall insulation in the UK hinges on factors such as your wall type and property type. Internal and external solid wall insulation jobs usually require around 100mm + of mineral wool or similar blanket insulation, whereas cavity walls require 150mm or more.

Akif has a keen interest in green home improvement solutions and the role of digital media in identifying climate trends. He aims to provide a multidisciplinary approach to content rooted in credible research and accuracy.
